Sketch the structure of the Transformer model. (2 points)
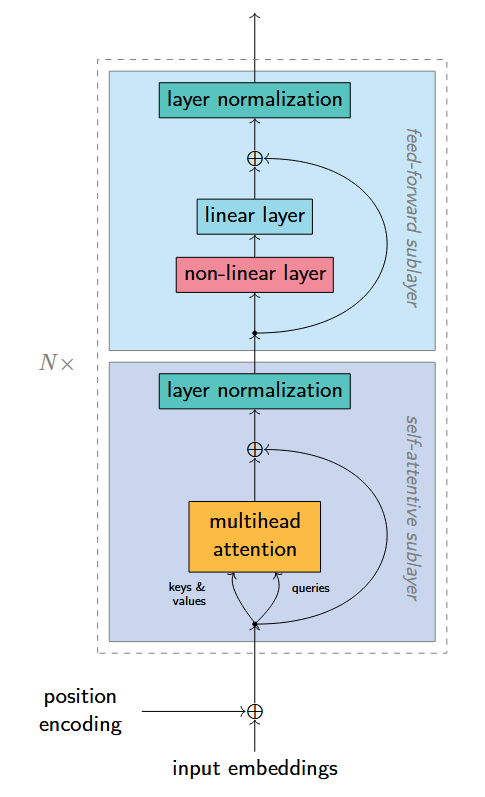
- author: Jindřich Libovický
- license: CC BY-SA
- there are several such layers
- each layer has two sublayers (self-attention and feed-forward)
What are the three basic properties of a probability function?
When do we say that two events are (statistically) independent?
Show how Bayes' Theorem can be derived.
Explain Chain Rule.
Explain the notion of Entropy (formula expected too).
Explain Kullback-Leibler distance (formula expected too).
Explain Mutual Information (formula expected too).
Explain the notion of The Noisy Channel.
Explain the notion of the n-gram language model.
Describe how Maximum Likelihood estimate of a trigram language model is computed. (2 points)
Why do we need smoothing (in language modelling)?
Give at least two examples of smoothing methods. (2 points)
What is a morphological tag? List at least five features that are often encoded in morphological tag sets.
List the open and closed part-of-speech classes and explain the difference between open and closed classes.
Explain the difference between a finite-state automaton and a finite-state transducer. Describe the algorithm of using a finite-state transducer to transform a surface string to a lexical string (pseudocode or source code in your favorite programming language). (2 points)
Give an example of a phonological or an orthographical change caused by morphological inflection (any natural language). Describe the rule that would take care of the change during analysis or generation. It is not required that you draw a transducer, although drawing a transducer is one of the possible ways of describing the rule.
ď:d <= _ +:0 e:ěkáď+e (lexical)kád0ě (surface)[ď:d | ň:n | ť:t] <=> _ +:0 [e:ě | i:i | í:í]Give an example of a long-distance dependency in morphology (any natural language). How would you handle it in a morphological analyzer?
u:ü <= _ c:c h:h +:0 e:e r:rBuch+er (lexical)Büch0er (surface)+:0 and perhaps test end of word (#)Describe dependency trees, constituent trees, differences between them and phenomena that must be addressed when converting between them. (2 points)
Give an example of a sentence (in any natural language) that has at least two plausible, semantically different syntactic analyses (readings). Draw the corresponding dependency trees and explain the difference in meaning. Are there other additional readings that are less probable but still grammatically acceptable? (2 points)
What is coordination? Why is it difficult in dependency parsing? How would you capture coordination in a dependency structure? What are the advantages and disadvantages of your solution?
What is ellipsis? Why is it difficult in parsing? Give examples of different kinds of ellipsis (any natural language).
Explain the difference between information need and query.
What is inverted index and what are the optimal data structures for it?
What is stopword and what is it useful for?
Explain the bag-of-word principle?
What is the main advantage and disadvantage of boolean model.
Explain the role of the two components in the TF-IDF weighting scheme.
Explain length normalization in vector space model what is it useful for?
Explain what a corpus is.
Explain what annotation is (in the context of language resources). What types of annotation do you know? (2 points)
What are the reasons for variability of even basic types of annotation, such as the annotation of morphological categories (parts of speech etc.).
Explain what a treebank is. Why trees are used? (2 points)
Explain what a parallel corpus is. What kind of alignments can we distinguish? (2 points)
What is a sentiment-annotated corpus? How can it be used?
What is a coreference-annotated corpus?
Explain how WordNet is structured?
Explain the difference between derivation and inflection?
Give at least two examples of situations in which measuring a percentage accuracy is not adequate.
Explain: precision, recall
What is F-measure, what is it useful for?
What is k-fold cross-validation?
Explain BLEU (the exact formula not needed, just the main principles).
Explain the purpose of brevity penalty in BLEU.
What is Labeled Attachment Score (in parsing)?
What is Word Error Rate (in speech recognition)?
What is inter-annotator agreement? How can it be measured?
What is Cohen's kappa?
Describe the two methods for training of the Word2Vec model.
Use formulas to describe how Word2Vec is trained with negative sampling. (2 points)
Explain the difference between Word2Vec and FastText embeddings.
Sketch the structure of the Transformer model. (2 points)

Why do we use positional encodings in the Transformer model.
What are residual connections in neural networks? Why do we use them?
Use formulas to express the loss function for training sequence labeling tasks.
Explain the pre-training procedure of the BERT model. (2 points)
Explain what is the pre-train and finetune paradigm in NLP.
Describe the task of named entitity recognition (NER). Explain the intution behind the CRF models compared to standard sequence labeling. (2 points)
Explain how does the self-attention differ in encoder-only and decoder-only models.
Why is MT difficult from linguistic point of view? Provide examples and explanation for at least three different phenomena. (2 points)
Why is MT difficult from computational point of view?
Briefly describe at least three methods of manual MT evaluation. (1-2 points)
Describe BLEU. 1 point for the core properties explained, 1 point for the (commented) formula.
Describe IBM Model 1 for word alignment, highlighting the EM structure of the algorithm.
Explain using equations the relation between Noisy channel model and log-linear model for classical statistical MT. (2 points)
Describe the loop of weight optimization for the log-linear model as used in phrase-based MT.
Describe the critical limitation of PBMT that NMT solves. Provide example training data and example input where PBMT is very likely to introduce an error.
Use formulas to highlight the similarity of NMT and LMs.
Describe, how words are fed to current NMT architectures and explain why is this beneficial over 1-hot representation.
Sketch the structure of an encoder-decoder architecture of neural MT, remember to describe the components in the picture (2 points)
What is the difference in RNN decoder application at training time vs. at runtime?
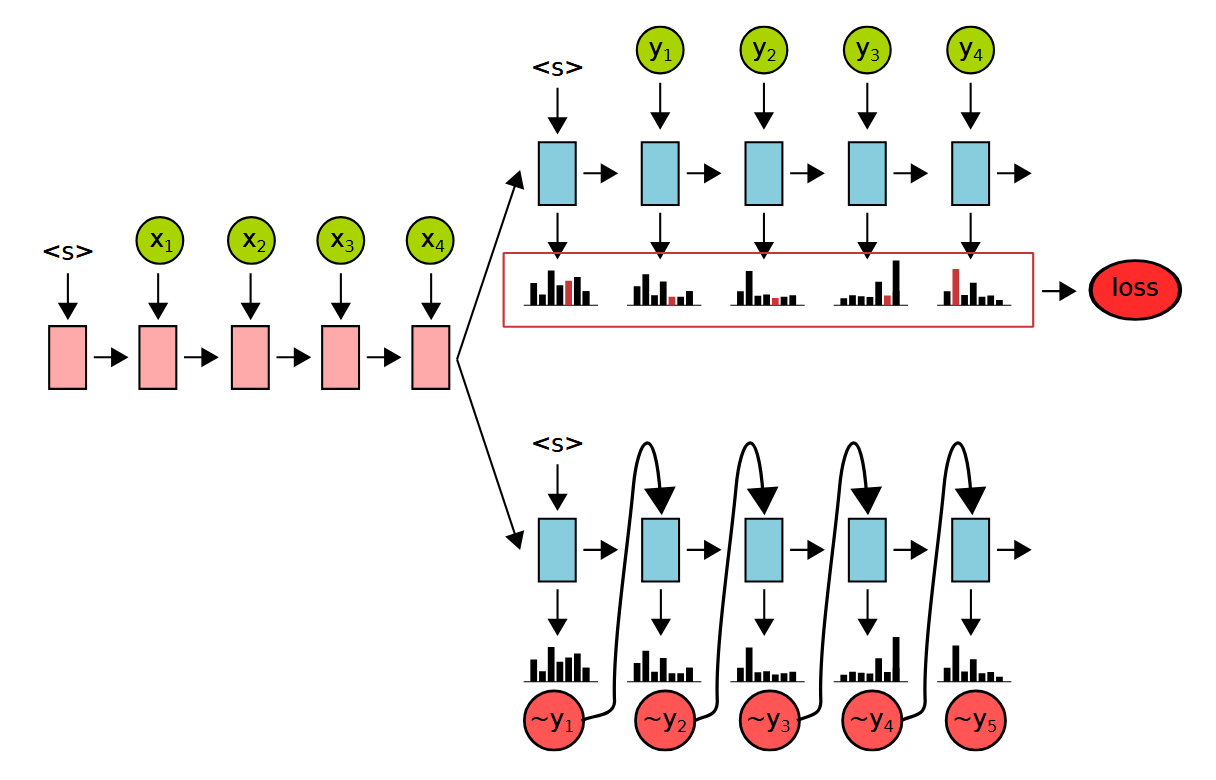
What problem does attention in NMT address? Provide the key idea of the method.
What problem/task do both RNN and self-attention resolve and what is the main benefit of self-attention over RNN?
What are the three roles each state at a Transformer encoder layer takes in self-attention.
What are the three uses of self-attention in the Transformer model?
Provide an example of NMT improvement that was assumed to come from additional linguistic information but occurred also for a simpler reason.
Summarize and compare the strategy of "classical statistical MT" vs. the strategy of neural approaches to MT.